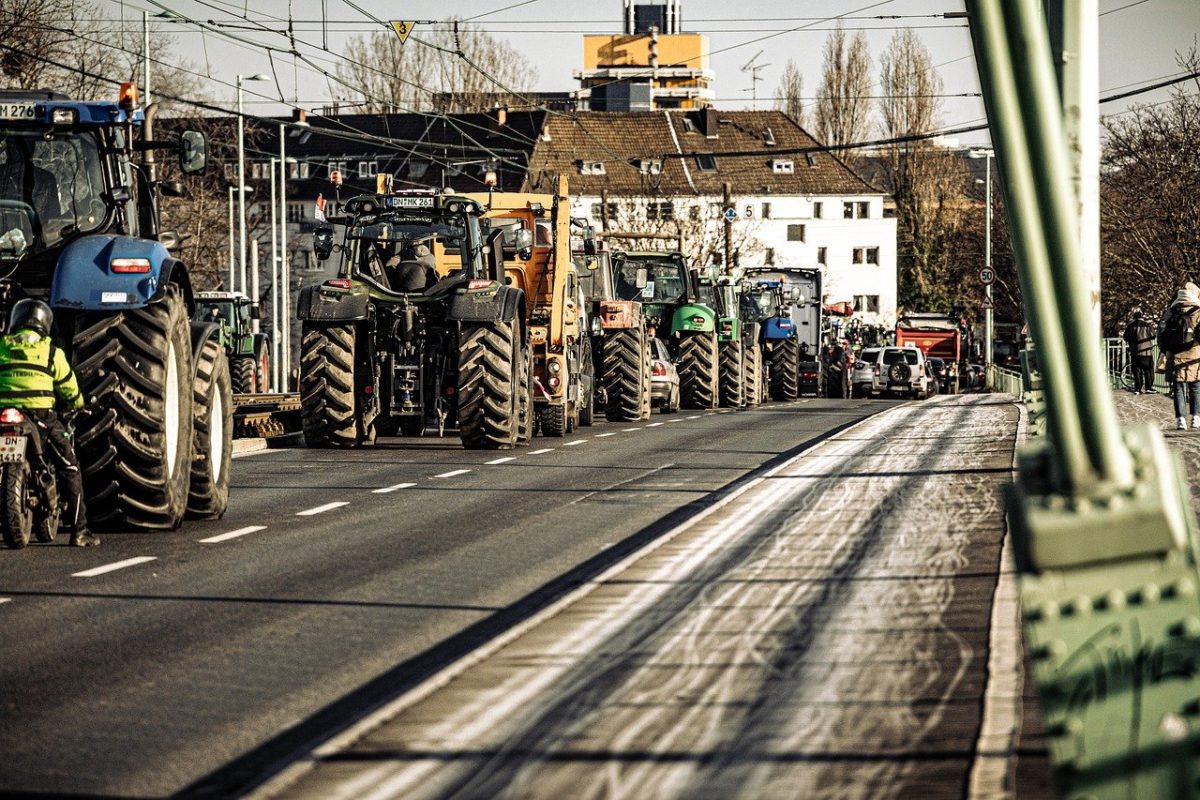
Recently, the agricultural sector has experienced significant unrest, manifesting in waves of farmer protests across the globe. Particularly prominent in the EU and India, these movements have been driven by a confluence of economic, environmental, and political challenges, reflecting broader concerns about sustainability, equity, and governance in the agricultural domain. This briefing note provides an overview of these protests, highlighting key examples, common themes and issues, and the wider political implications.
Navigating the Era of Gerontocracy: Health, Age, and Political Stagnation
Lately, the remarkable strides in medical science have undeniably enhanced the quality and expectancy of human life. This triumph, however, has ushered in an unintended consequence in the political arena, leading to the emergence of a gerontocracy—a governance system where the elderly hold significant power and influence. This phenomenon raises pertinent questions about the interplay between health, age, and political stagnation, and how these factors shape governance in various nations across the globe.
The term ‘gerontocracy’ originates from the Greek words ‘geron’ meaning old man and ‘kratos’ meaning power. It aptly describes a situation where leadership is predominantly in the hands of an older generation, often resulting in a resistance to change and innovation. This is particularly poignant in today’s fast-paced world, where adaptability and technological savvy are paramount.
Continue reading “Navigating the Era of Gerontocracy: Health, Age, and Political Stagnation”Pakistan: Situational update & digital campaign analysis
Summary
- The vote count for Pakistan’s recent election has concluded, with Imran Khan’s allies winning the most seats in the National Assembly, but not enough to form a majority.
- With no single party having enough seats to create a government independently, hopes of ending political turmoil are dampened. Khan’s party has declared victory and is urging all institutions to respect its mandate.
- However, there have been protests and petitions challenging the election results, and foreign governments have expressed concerns about irregularities and manipulation.
- Khan’s populist rhetoric and the country’s internet-savvy youth are reshaping Pakistani politics. His party used social media and AI to reach voters and mobilize support, bypassing state censorship.
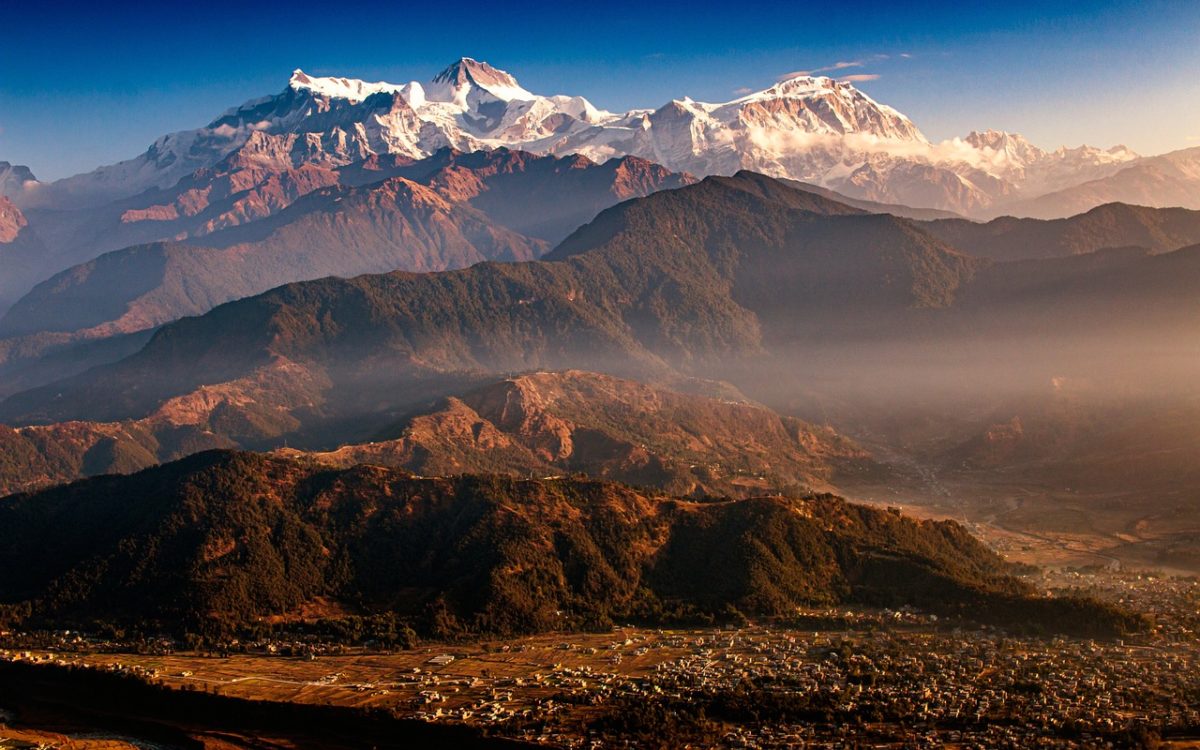
Interconnected: The electrical grids of India, Bhutan, and Nepal
Summary
- While the electrical grids of India, Bhutan, and Nepal aren’t fully synchronized as a single system, they are interconnected through various points and agreements, allowing for electricity exchange.
- As landlocked and mountainous countries, Nepal and Bhutan have limited options to industrialize, but have hydropower potential. Electricity can be an important export for both.
- The electrical grid connections facilitate the trade in electricity and contribute to regional energy security. Countries like Nepal and Bhutan export surplus electricity and import energy during periods of deficit, thereby supporting their energy needs and economic development.
- These interconnections between India, Bhutan, and Nepal have spurred significant geopolitical and domestic political issues within the region, largely shaped by strategic interests, economic dependencies, and environmental concerns.
PPM Newsletter
We’ve moved our newsletter, formerly hosted on Substack, to this blog.
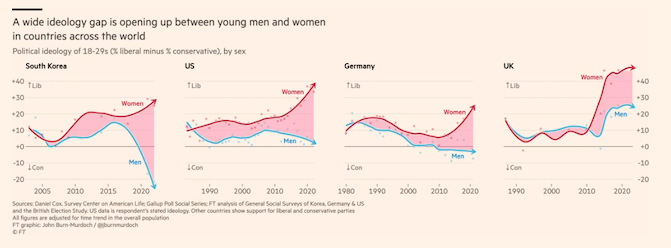
The (youth) gender divide
Young voters have been a constant theme for this newsletter. One article published recently has caused a great deal of controversy by suggesting that, contrary to popular belief, Gen Z can actually be considered as two distinct groups rather than one. Specifically, women aged 18 to 30 are significantly more liberal compared to their male counterparts [paywall]. This marks a shift from previous decades where both genders were relatively evenly distributed across liberal and conservative ideologies. In fact, the difference in liberal views between women and men in this age group is as high as 30%.
Rising Tides of Controversy: Navigating the India-Maldives Spat
The latest controversy between India and the Maldives primarily revolves around a series of events that have strained the diplomatic relations between the two nations. The controversy was ignited by negative remarks made by three deputy ministers in the Ministry of Youth Affairs in the Maldives about Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi. These remarks were made in response to Modi’s visit to Lakshadweep and were perceived as a challenge to the Maldivian tourism industry, which is renowned for its beachside amenities.
The Indian government raised this issue with the Maldives, resulting in the suspension of the three ministers by the Maldivian government.
Continue reading “Rising Tides of Controversy: Navigating the India-Maldives Spat”Indonesian elections: situational brief
Summary
The 2024 Indonesian presidential election will involve a complex interplay of economic challenges, political legacies, and the rising influence of young voters.
- The Economy: The main worries for the people in Indonesia are inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. These problems have got worse because of global events like the US Federal Reserve’s monetary policy and the war in Ukraine.
- Political Dynasties: Political dynasties have also become a critical issue, with President Joko Widodo’s son running as a vice-presidential candidate, sparking debates about the role of political dynasties in Indonesian politics.
- Youth vote: Young voters, including Gen Z and Millennials, will play a significant role in the election, with their concerns about employment and climate issues influencing their voting decisions. The use of social media platforms like TikTok in political campaigning is also indicative of a shift in election dynamics.
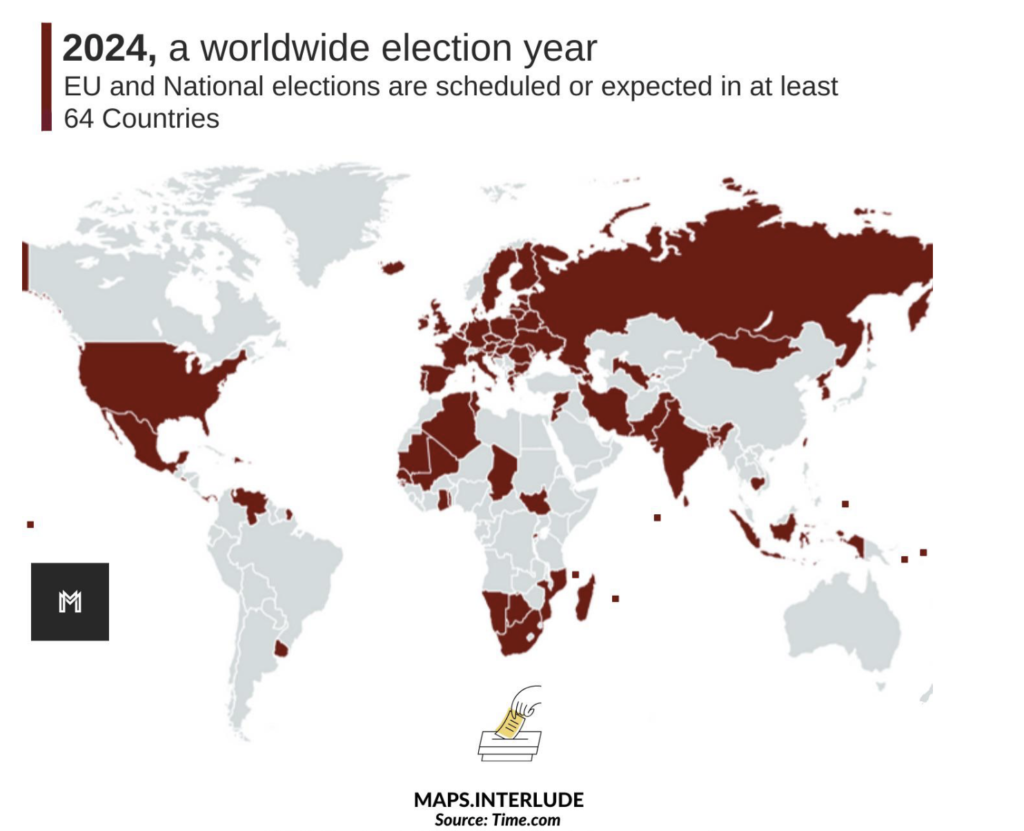
The Year of Elections.
Welcome to 2024! Our team is eagerly looking forward to what has been dubbed “The Year of Elections.”
Pakistan: situational brief
Summary
- Pressures and vulnerabilities: Pakistan faces a precarious economic situation. Growing trade imbalances, high inflation, and a depreciating rupee threaten stability. The IMF loan program offers vital support, but demanding austerity measures fuel public discontent.
- Political turmoil: Imran Khan’s PTI party faces challenges, including disputes with the Election Commission of Pakistan (ECP) that could impact its standing in the upcoming election. Other parties like PML-N and PPP are seeking alliances to increase their chances of forming the next government.
- Military’s influence: The Pakistani military continues to wield significant influence, with concerns about its behind-the-scenes role in political manoeuvring. Balancing civilian aspirations with the military’s interests remains a delicate task.
- Moving Forward: Pakistan’s path ahead hinges on balancing economic reforms with social needs, tackling corruption, and ensuring credible elections. Navigating complex international relations with regional players and managing security concerns along the Afghan border are further hurdles.
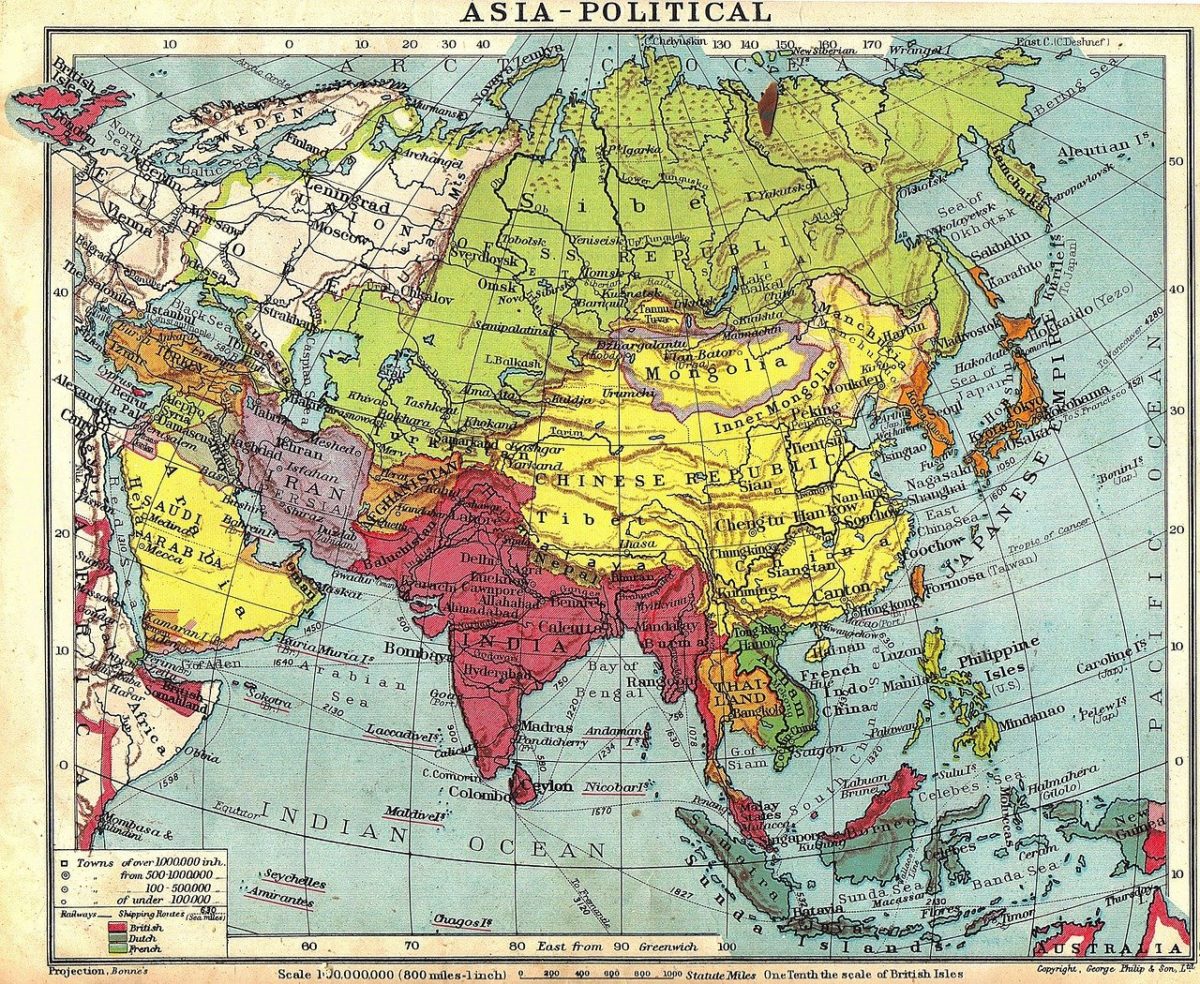
Young voters in Asia
Young voters in Asia are emerging as a critical demographic in shaping electoral outcomes. In the upcoming 2024 Indonesian general election, for instance, millennials and Gen-Z voters comprise more than half of the eligible voting population. This significant proportion underscores their potential to decisively influence the presidential and legislative elections.
In Taiwan, whom young people ultimately vote for — and how many vote at all — could be crucial in deciding the presidential election on Jan. 13. About 70% of Taiwanese in their 20s and 30s voted in the 2020 presidential election, a lower share than among middle-aged and older voters, according to official data. People ages 20 to 34 count for one-fifth of Taiwan’s population, government estimates show.
Meanwhile, in India, there has been an ongoing concern about the number of young people who are eligible to vote but do not. Prime Minister Modi took to Twitter before the recent state elections to encourage young and first time voters.
Continue reading “Young voters in Asia”